Understanding Septal Infarct: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Septal infarct is a medical condition that occurs when there is damage to the septum, which is the wall dividing the left and right sides of the heart. It is often a result of reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to inadequate oxygen supply. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for septal infarct.
What Causes Septal Infarct?
Septal infarct usually occurs as a consequence of a coronary artery blockage, typically caused by atherosclerosis or the buildup of plaque within the arteries. When the blood flow to the septum is restricted, it leads to inadequate oxygen supply, resulting in damage to the heart muscle. Other factors that can contribute to septal infarct include hypertension, smoking, diabetes, and high cholesterol levels.
Recognizing the Symptoms:
Septal infarct often presents with various symptoms, including chest pain or discomfort. The pain may radiate to the left arm, neck, or jaw, resembling the symptoms of a heart attack. Shortness of breath, fatigue, and lightheadedness are also common indicators. However, it’s important to note that symptoms can vary from person to person, and some individuals may not experience any symptoms at all.
Diagnosis of Septal Infarct:
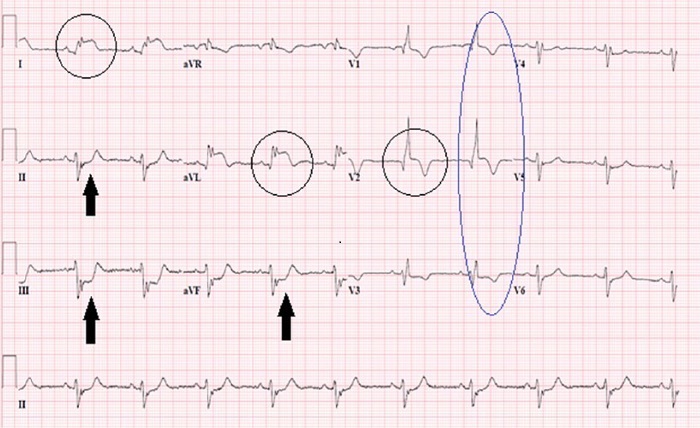
To diagnose septal infarct, healthcare professionals employ a combination of clinical evaluations, medical history assessments, and diagnostic tests. Electrocardiography (ECG) is one of the initial tests performed, as it can detect abnormalities in the heart’s electrical activity. An echocardiogram provides detailed images of the heart, helping identify any structural abnormalities. Additionally, cardiac stress tests, coronary angiography, and blood tests may be conducted to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the extent of damage.
Treatment Options:
The primary goals of treating septal infarct are to restore blood flow to the affected area, prevent further damage, and manage symptoms. The specific treatment plan depends on the severity of the condition and the patient’s overall health. Medications such as antiplatelet agents, beta-blockers, and nitroglycerin may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. In more severe cases, revascularization procedures like percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) may be necessary to restore blood flow to the heart.
Lifestyle Modifications:
In addition to medical interventions, making certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve the prognosis and reduce the risk of recurrent septal infarct. Quitting smoking, adopting a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing conditions like hypertension and diabetes are crucial steps in preventing further damage to the heart.
Rehabilitation and Follow-Up:
Cardiac rehabilitation programs play a vital role in the recovery process after septal infarct. These programs focus on lifestyle modifications, exercise routines, and emotional support to help patients regain their strength and reduce the risk of future cardiac events. Regular follow-up visits with healthcare providers are essential to monitor progress, adjust treatment plans if needed, and ensure optimal heart health.
Conclusion:
Septal infarct is a condition characterized by damage to the septum due to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. Early recognition of symptoms, prompt diagnosis, and appropriate treatment are crucial in managing this condition effectively. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, adhering to prescribed medications, and attending cardiac rehabilitation programs, individuals can enhance their overall well-being and reduce the risk of complications associated with septal infarct. If you experience any symptoms or have concerns about your heart health, it is important to seek medical